
You probably already know that an engine or motor makes your car go, but what exactly is an engine? Is it the same as a motor? And how do they work? If you have a curious mini car lover in your life, read on to learn more.
What are engines and motors?
Engines and motors can seem complicated, but their definition is simple: They are machines that turn energy into movement. That’s it! There are many different types of engines and motors, but they all use some form of energy to move things around.
What's the difference between an engine and a motor?
The words motor and engine can be used interchangeably. Technically, however, there is a difference!
Engines use heat to power movement. They convert fuel from sources like gas, diesel, or coal into energy. Steam engines and the internal combustion engine are great examples of this! Steam engines were manufactured starting in the 1800s and were used to power early cars, trains, and ships up until the 1960s. They would use coal as fuel, which was very heavy and required a lot of manual labor. Over time, steam engines were replaced with internal combustion engines, which use gas or diesel and are more energy efficient.
Motors use electricity to create magnetic fields that power movement. Unlike engines, electric motors don’t need fuel like gas, diesel, or coal as they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. We don’t usually think much about electric motors, but you almost certainly have one right in your home! Electric motors power washing machines, blenders, and even remote-controlled toy cars! These days, more powerful motors with stronger magnetic fields are used inside electric vehicles, trains, and subways.

How does an internal combustion engine work?
The internal combustion engine powers many of our day-to-day activities, from the family vehicle that gets you to soccer practice or music lessons to the trucks that bring our food from the farm to supermarket shelves. So, how exactly does it work? As the name suggests, the internal combustion engine creates energy by burning or combusting fuel inside of a cylinder. This process happens in 4 parts or ‘strokes.’
Before we jump into how this cycle works, we need to know about a couple of engine parts: the piston and the crankshaft. Simply put, the crankshaft revolves to move the engine through the different strokes, and the piston moves up and down to open and close valves.
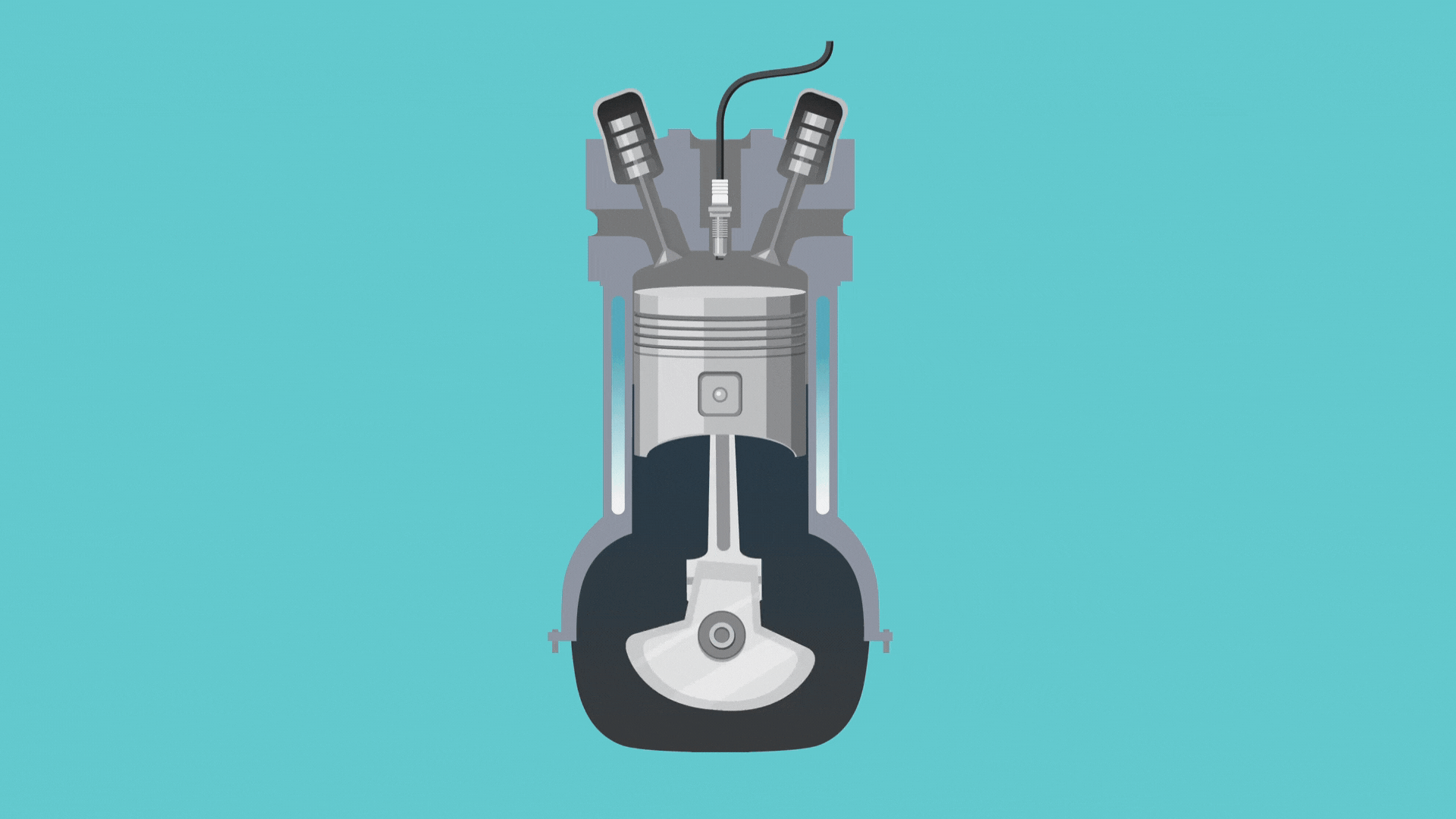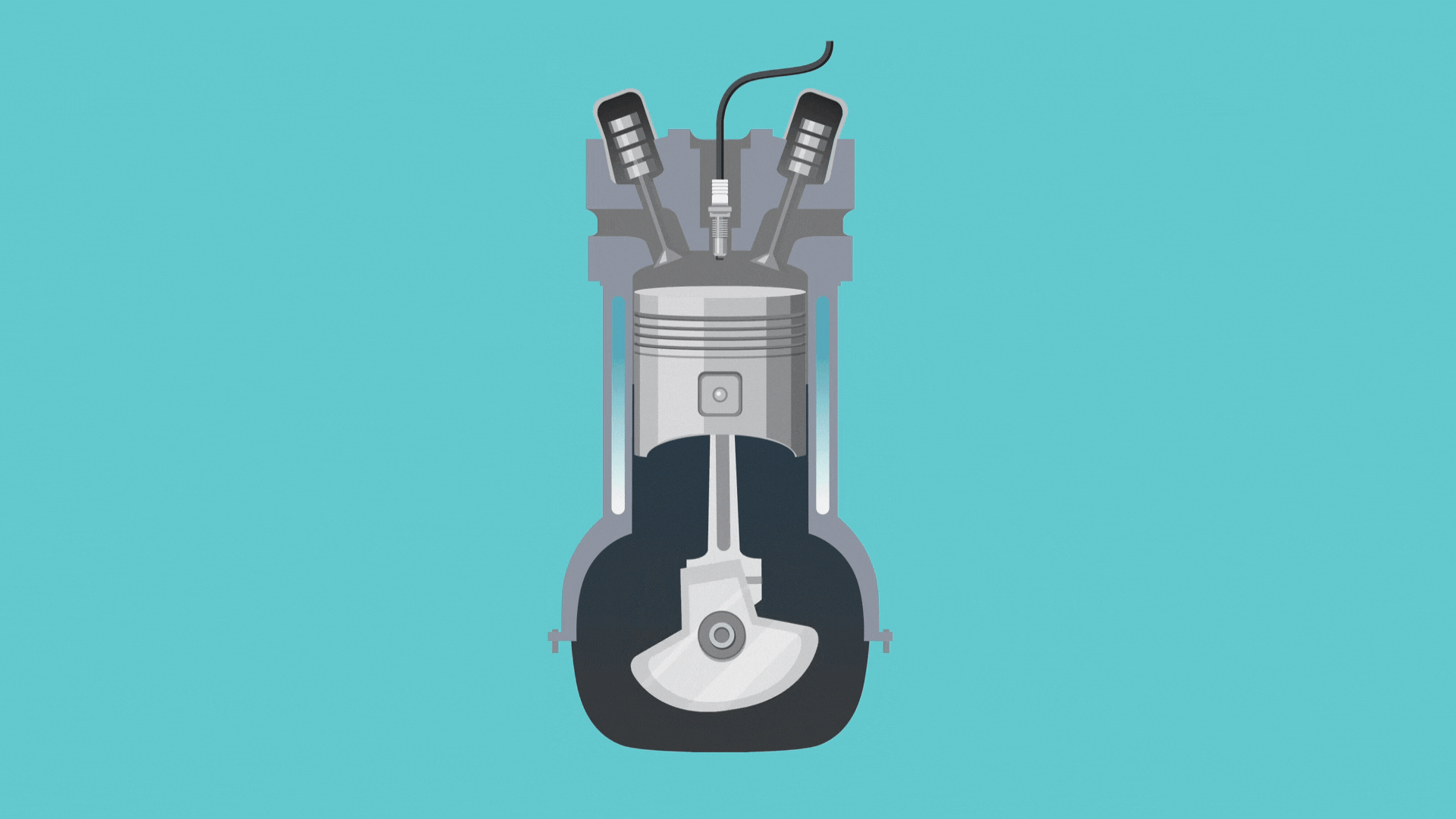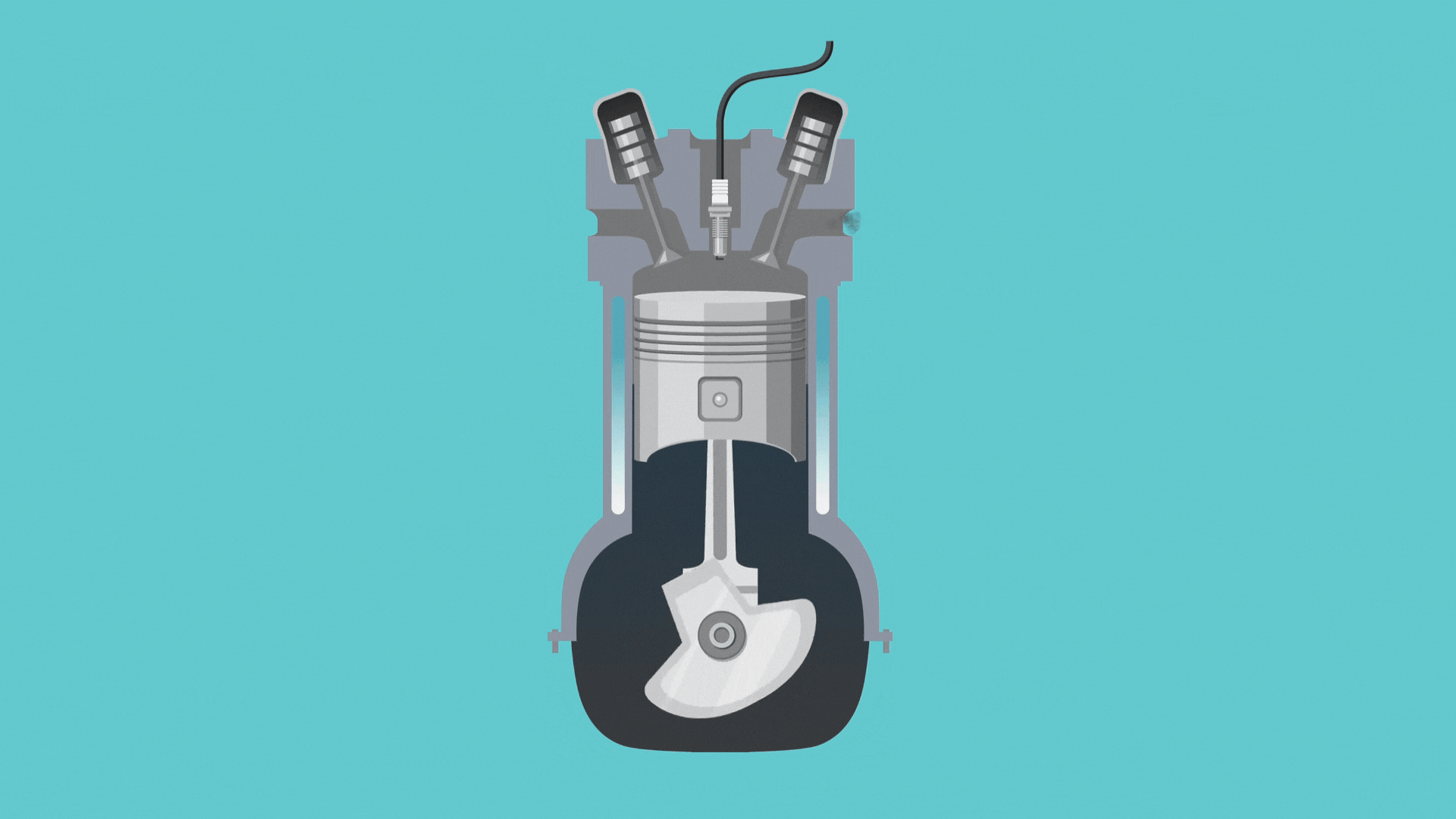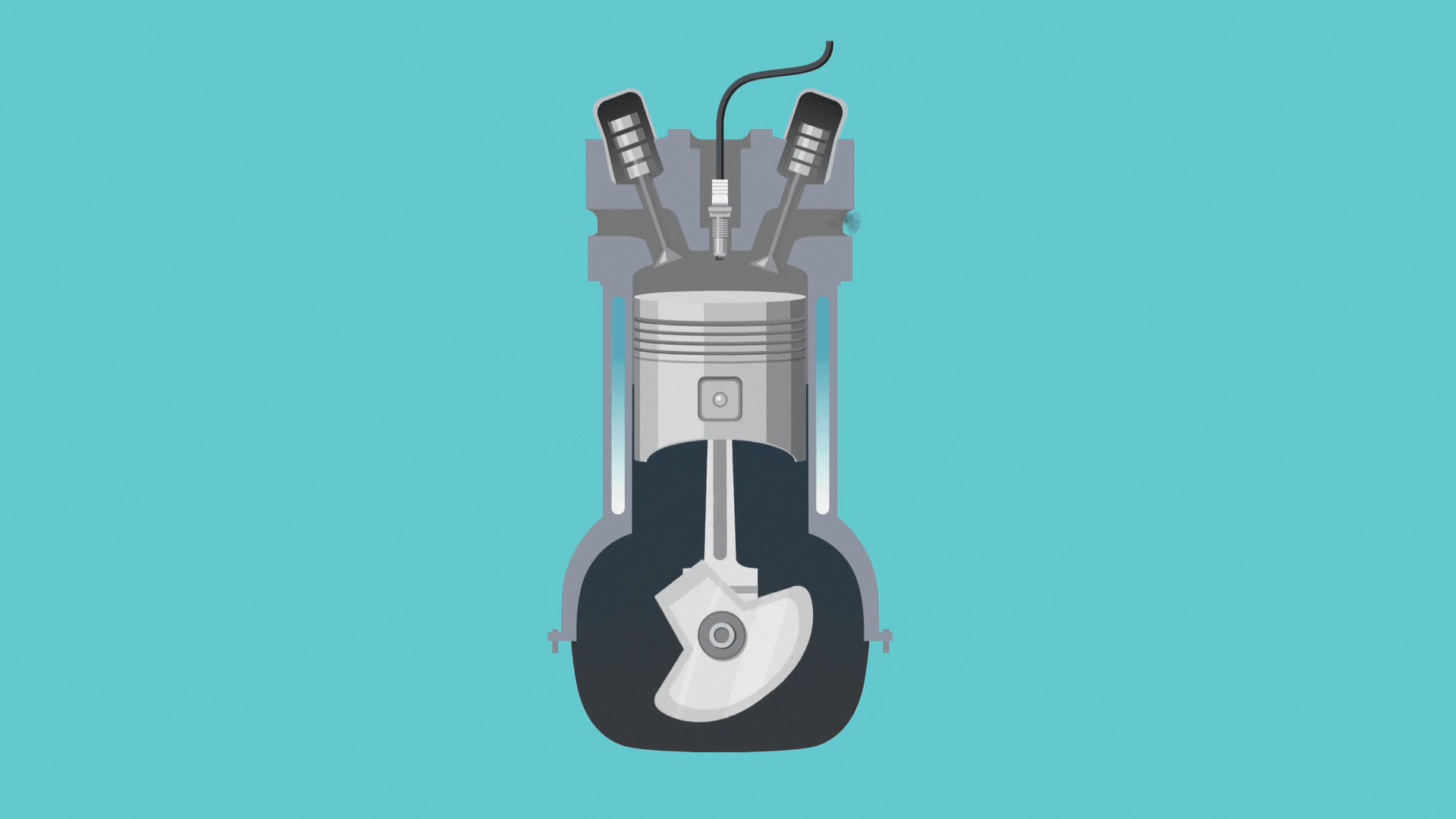
- The intake stroke: In this first part of the cycle, the crankshaft moves the piston to open the intake valve. This allows a tiny bit of gasoline and lots of air to enter the cylinder.
- The compression stroke: Here, the piston moves again to compress the air and gas.
- The combustion stroke: Once the cylinder’s contents are compressed, the engine sparks, and the gasoline explodes, moving the piston back down.
- The exhaust stroke: Finally, the piston moves again and opens the exhaust valve so the exhaust fumes can travel out of the tailpipe.
And that’s it! Once the engine finishes the four strokes, it goes back to step one and repeats the cycle again and again, creating the movement that gets us from point A to point B.
How does an electric motor work?
From the road to the kitchen counter, electric motors are everywhere if you take a closer look. Electric motors come in many sizes, but at their core, they all use magnets to create movement!
There are two types of electric flow that power electric motors. Small motors, like those found in common kitchen appliances, use DC (direct) current, while more powerful electric motors, like those used to power cars, use AC (alternating) current. As the name suggests, direct current flows in one direction while alternating current moves back and forth, making it more powerful.
The most common type of motor used to power electric cars today is called an asynchronous (or induction) motor. To learn how an electric motor works, let’s take a closer look at what parts are under the hood:

Charge port: This is where electric flow enters the vehicle when plugged in at a charging station. Electric vehicle owners can have a charging station right at their own house or go to a commercial charging station nearby. Did you know a standard outlet can charge an entire electric car overnight? After the charge port receives electric flow from the grid, it is sent to the traction battery pack.
Inverter: But wait! Electric flow doesn’t exactly go straight from the charge port to the battery pack. First, there is an important step it must go through. After the driver plugs in their car to charge it up, the electric flow is in the form of DC or direct current. The inverter’s job is to convert DC current into AC current.
Traction Battery Pack: The job of the battery pack is pretty simple: store energy received from the inverter. Electric vehicles on the road today almost always use a lithium-ion battery.
Electric Traction Motor: Finally, the traction motor draws AC current from the battery pack to start working! Electric vehicles today use a type of motor called a three-phase AC induction motor. This means that they use three waves of AC electric flow at the same time. There are three main parts of an AC electric motor: the stator, the rotor, and the squirrel cage (it’s called that because it looks like a giant hamster wheel!). On the outside, the motor looks like a long drum or cylinder, which is hollowed out inside. The stator is stationary, meaning it doesn’t move. The rotor rotates inside the stator on a shaft in the squirrel cage. To make the rotor rotate, both components have electromagnets arranged in a reverse polarity.

To understand how the stator makes the rotor spin, let’s take a quick look at how magnets work. Every magnet has a north pole and a south pole. When placed next to each other, two opposite poles will attract (north/south) while two similar poles repel (north/north, south/south).
The stator receives AC power from the battery pack, which activates its magnets. This, in turn, activates the magnets in the rotor as their opposing poles attract. The attraction of the opposing magnetic poles between the stator and the rotor causes the rotor to start rotating inside the squirrel cage. This high-speed rotation creates a powerful magnetic field and torque that powers electric vehicles everywhere they need to go!
And there you have it! Motors and engines power so much around us – from simple kitchen appliances to vehicles big and small.
What does your little one want to know about vehicles? Share your questions with us on social media @driventoys. And remember to subscribe to our newsletter for exciting updates and promotions! Roll into a world of endless possibilities with DRIVEN.




